Vitamin B5, or pantothenic acid, is one of the eight B vitamins that make up the B complex. Like all B vitamins, vitamin B5 is water-soluble and aids in converting carbohydrates into glucose to produce energy that fuels the body. Found in plants, animals, and humans, pantothenic acid is essential to most all forms of life.
According to MedlinePlus, pantothenic acid is found in the coenzyme A, which is necessary for many chemical reactions, and healthy levels of vitamin B5 are necessary to help the body use fats and proteins and promote the body’s overall well-being.
What is Vitamin B5?
Pantothenic acid is the forerunner for the synthesis of the coenzyme A (CoA), which is necessary for all life forms. Coenzyme A and its acyl derivatives are used by the body to generate energy from dietary fat, proteins, and carbohydrates.
CoA is also used in the citric acid cycle to synthesize fats, steroid hormones (estrogen and testosterone), vitamins A and D, acetylcholine (neurotransmitter used to signal the immune system and organs), and in β-oxidation. With these processes, the body can sufficiently break down dietary nutrients from food to produce energy.
Vitamin B5 Health Benefits
It seems the list is endless when assessing the benefits of pantothenic acid for the body. In conjunction with other B vitamins, the body uses the vitamin to fuel the body in several different ways. Vitamin b5 uses affect the brain, heart, adrenal glands, skin, and hair heavily depend on the vitamin to function.
Vitamin B5 has been used to treat and aid in the function of several bodily processes. Nerve function, cardiovascular health, adrenal gland function, acne and skin blemishes, wound healing, and hair loss or thinning.
Imbalance associated with the adrenal glands and secretions of hormones, such as stress, immune function, and weight loss or obesity have also been treated with an intake of pantothenic acid.
Although pantothenic acid does not often treat the source of the symptoms, it is used to alleviate symptoms often associated with chemical/ hormonal imbalance within the body. Not only does it aid in treating these symptoms, a healthy dose or intake of pantothenic acid will also help prevent some symptoms by encouraging overall health of the body.
Vitamin B5 for Brain and Nerve Function
A healthy brain is essential for daily life and responsible for transmitting information to the rest of the body. Pantothenic acid creates acetylcholine- a chemical essential for the nervous system.
Without acetylcholine, the body would not be able to signal the immune system and organs. Pantothenic acid is also beneficial to the brain and headaches or migraines, and alcohol dependence.
Vitamin B5 for Cardiovascular Health
Resembling coenzyme A, pantethine administration has proven to decrease cardiovascular issues.
The development and production of new red blood cells are dependent upon vitamin b5 intake; increased circulation of vitamin B5 can also enhance red blood cell transmission. Pantothenic acid also aids in the ability for vitamin B2 to mobilize iron, which prevents iron deficiency symptoms such as, fatigue and shortness of breath.
Vitamin B5 and the Adrenal Glands
Arguably one of the most important functions of pantothenic acid is the effects on the adrenal glands. Evidence suggests that vitamin B5 is directly responsible for aiding in hormone production.
These glands control several hormone functions within the body.
It is also helpful in regulating cortisol. Although too much cortisol within the body can negatively affect metabolism, the body requires small amounts to manage metabolism and a healthy weight.
According to Physiology, adequate vitamin B5 reduces the chance of adrenal fatigue or exhaustion. When this occurs, stress levels cannot be maintained and negatively impact the rest of the body. If fatigue or exhaustion of the adrenal glands occur, pantothenic acid can replenish and reboot the glands. Thus, improving one’s response to stress.
Vitamin B5 Benefits Weight Loss
Although a vitamin B5 supplement or excess intake of pantothenic acid will not directly result in weight loss, the vitamin is responsible for ensuring proper metabolism and digestion of foods. The main function of vitamin B5 is to metabolize food to energy.
With more energy and stamina, one can exercise without becoming fatigued quickly, rebuild tissue and muscle, and maintain a healthy weight once the desired amount is achieved. With the metabolic processes and boosts of energy and immunity of pantothenic acid, supplements or a highly inclusive diet of vitamin B5 can promote healthy overall well-being that leads exertion of energy to exercise and normal metabolism to aid in weight loss.
Vitamin B5 Benefits for Skin
Vitamin B5 for Acne
By properly using carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids, Vitamin B5 plays a substantial role in the elasticity, healing, and aging of the skin. Pantothenic acid reduces signs of premature aging and enhances the overall integrity of the largest organs in the body, skin. Vitamin B5 has also been proven to assist in wound healing; taken orally or applied topically, closure of wounds appeared to occur at a more rapid pace than without the supplement. In addition to healing of wounds, increased integrity of scar tissue has also been documented.
Studies prove that inflammation and tissue repair were significantly greater with a vitamin B5 supplement. The liquid form of vitamin B5 known as, dexpanthenol, D-pantothenyl alcohol, D-panthenol, or panthenol can also be purchased. These can be used topically or injected for wound healing. Dermatologists also use vitamin B5 to help treat inflammation of the skin and acne breakouts.
Oral and topical treatments have proven to decrease oil and sebum secretion in patients within 2-3 days. After two weeks of treatment, patients will notice a change in pore size and acne lesions will begin to heal and disappear.
Eight weeks following initial treatment, patients begin to notice breakouts are controlled and minimal. Pantothenic acid decreases stress-induced acne outbreaks and heals the skin from previous acne occurrence.
Vitamin B5 for Hair
Doctors have also suggested a vitamin B5 supplement for thinning or loss of hair. A deficiency of the pantothenic acid can also cause premature graying of hair in addition to thinning and loss.
Cosmetic industries have begun adding the vitamin to shampoos, but no evidence has proven this type of topical wash is beneficial. As a supplement, the vitamin will improve the health status of the scalp and encourage new hair growth, as well as, strengthen the hair follicles.
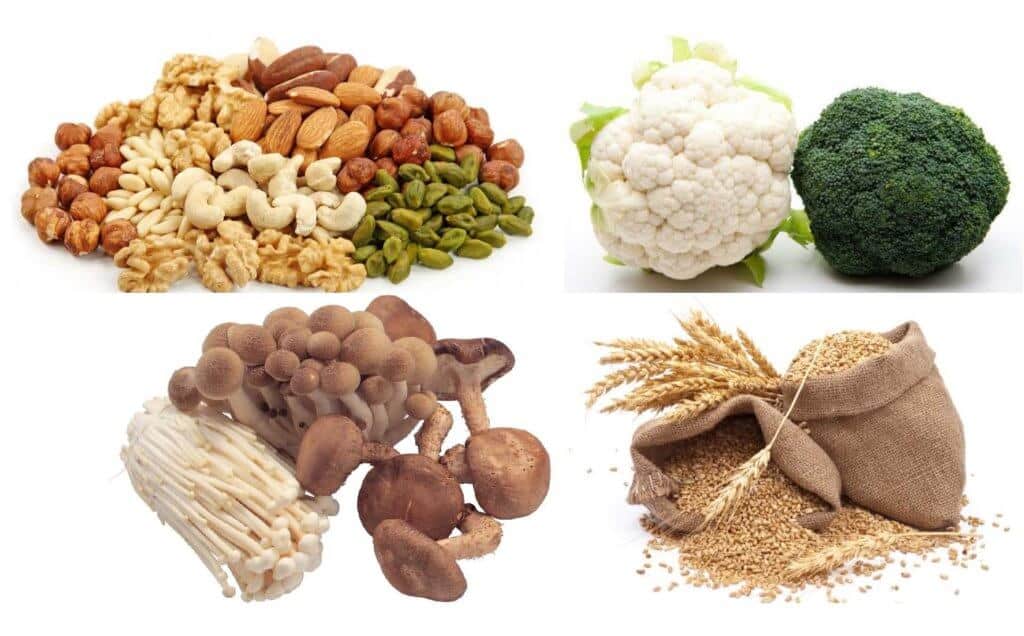
Sources of Vitamin B5
Pantothenic acid derives from the Greek root, pantos, meaning “from everywhere” because the vitamin is found in several different fruits, grains, seeds, protein, dairy products, and much more.
Usually available in foods as a component of coenzyme A and phosphopantetheine, during ingestion, the dietary coenzyme A and phosphopantetheine break down by chemical reaction to water, or hydrolyzed, to pantothenic acid.
Grains are an excellent source of pantothenic acid; however, the refining process often skins the grain where most of Vitamin B5 is located and can result in a 35%-75% loss.
In addition to the refinement process of grains, canning for the preservation of fruits and vegetables can also lead to a decrease in the vitamin.
Vitamin B5 Foods List
Eating a diet that consists of a sufficient amount of vitamin B5 boosts the immune system, encourages adrenal gland and neural functions, and aids in several other benefits for the body.
Foods with the highest amount of pantothenic acid include:
Proteins
- Animal liver
- Fish/ Shellfish/ Lobster
- Duck
- Veal
- Turkey
- Chicken
Vegetables
- Broccoli
- Cabbage
- Cauliflower
- Corn
- White and Sweet Potatoes
- Collard Greens
- Kale
Dairy Products
- Yogurt
- Milk
- Feta cheese
- Eggs
Legumes/ Nuts
- Split Peas
- Lentils
- Soybeans
- Peanuts
- Almonds
- Fruits
- Avocado
- Orange
- Tomato
Grains
- Whole Wheat Bread
- Whole Grain Cereal
- Sunflower Seeds
- Wheat Bran
Mushrooms
- Shiitake Mushroom
- Crimini Mushroom
Vitamin B5 RDA
Pantothenic acid (vitamin b5) recommended daily allowance (RDA) intake varies by age, but with a healthy diet is easily attainable. For infants, around 2 mg is preferred. Young children should average an intake of 3 mg- 4 mg.
Breastfeeding and pregnant women should aim to intake around 6 mg-7 mg to ensure a healthy pregnancy and lactation. On average, an adult should seek around 5-6 mg of vitamin B5 per day, NutriFacts states.
Vitamin B5 Supplements
How Much Vitamin B5 Should I Take?
Pantethine, the disulfide form of pantothenic acid (vitamin B5) is available as a dietary supplement. The supplement pantethine is considered a more active form of pantothenic acid because it contains the sulfhydryl-group necessary for co-enzyme A but does not store better for the consumer so calcium pantothenate supplement, another form of pantothenic acid administered, is preferred.
Also, calcium pantothenate is a more stable form in the ingestion and intestinal tract because it is salt. It is also prescribed or suggested by physicians as a dietary supplement in 5 mg- 10 mg doses.
Supplementation has been considered a more homeopathic and natural solution to several bodily processes that have gone awry.
Vitamin B5 Benefits for Men
Men, specifically, can benefit greatly from a diet enriched with vitamin B5. The adrenal glands rely heavily on vitamin B5 to help initiate the creation of testosterone, a steroid hormone found more prominently in men.
Testosterone aids in muscle stamina, sexual function, and physicality of men. Pantothenic acid is also used to treat an enlarged prostate. With a vitamin B5 deficiency, testosterone levels will suffer and result in several symptoms such as:
- Increased body fat
- Reduced sexual desire
- Decreased muscle mass and strength
- Infertility
- Lack of body hair
- Increased fatigue
Vitamin B5 Benefits for Women
Just as the adrenal glands are responsible for some of the testosterone levels in men, women are also dependent upon the glands to encourage production of estrogen, as well as progesterone.
Also, oral contraceptives that contain estrogen and progestin do increase the need for vitamin B5 within the body to help balance the artificial and naturally produced hormones within the body. In tests, it has been found that women taking oral contraceptives had a decreased amount of pantothenic acid. The contraceptives increase the metabolism and break down of pantothenic acid within the body.
Breastfeeding and pregnancy can also affect the vitamin b5 levels in women, and place them at risk for deficiency. Optima vitamin b5 levels are necessary for a healthy pregnancy for both the mother and child.
According to MedlinePlus, adrenal gland function reduces fatigue, stress, and weight gain. Healthy adrenal glands will reduce environmental stresses associated with menstrual cycles, motherhood, and other environmental influences.
Vitamin B5 Side Effects
According to Mount Sinai, Vitamin B5 is generally not toxic in humans. Although there is no scientific evidence to support an overdose, one can experience:
- Gastrointestinal discomfort
- Nausea
- Heartburn
- Diarrhea
- Stomach cramps
Symptoms of Vitamin B5 Deficiency
It is rare for humans to experience vitamin B5 deficiency symptoms with supplements available and a generally nutritious diet, but studies have proven in chronically stressed or malnourished individuals symptoms of pantothenic acid can occur. The widespread presence of vitamin B5 in most foods reduces the likelihood of a deficiency.
However, some medications can also prohibit the function of breaking down carbohydrates in the intestinal tract and disrupt the vitamin B5 levels within the body. Minor symptoms of vitamin B5 deficiency can include: irritability, and muscle cramps. A vitamin B5 deficiency can also cause an irritated gastrointestinal tract with symptoms such as:
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal pain
According to NCBI, due to the influence on the immune system, a deficiency in vitamin B5 can also cause upper respiratory infections, as well as, difficulty healing or weakened ability to fight illness. In some extreme and rare cases, vitamin B5 deficiency has had more severe symptoms including adrenal insufficiency or exhaustion and hepatic encephalopathy, or toxins in the blood. While these symptoms may be more advanced, each is reversible with correct supplement treatment.
What Users Are Saying
“This has worked miracles on my skin and cystic acne. Doctors best kept secret I guess. I discovered this after doing a lot of research on proper supplementation for cystic acne as it’s not treated topically, but internally. I take 3-4 per day, all at the same time, and within a week I noticed my acne disappearing.”
“Did nothing for my acne. Caused major hairloss, even after weeks/months of not taking it. Not worth it. My hair is thin, brittle and I lose at the minimum 50 hairs a day and they grow back thinner.”
“I bought this product soley on the purpose of clearing my skin and it works. I seen a lot of reviews off of YouTube claiming that taking B5 it will clear your skin, so I bought it and it has worked!”
Bottom Line on Vitamin B5
Research shows that vitamin B5 can be a useful dietary supplement for some individuals. The compound, found in many common foods and drinks, is a necessary component to basic human health, as it plays a role in many different bodily processes. However, consuming too much of the vitamin through supplementation can lead to some negative side effects.
Additionally, there is little evidence that shows vitamin B5 can help aid in active weight loss. In that case, it may be best to choose a program that can be individualized to the dieter’s needs.
Noom is one of the best weight-loss programs we’ve seen yet because of its many interactive features, like human coaching sessions, food tracking, and custom meal plans.
Noom is offering all readers a free trial offer of their program so you can give it a try risk-free.
Vitamin B5 | Benefits of B-Vitamins Questions & Answers
- Recent:
Low vitamin B5 can cause symptoms such as fatigue, muscle cramps, nausea, headaches, and insomnia. It may also cause anemia due to decreased red blood cell production. Additionally, low levels of vitamin B5 may impair cognitive functions such as memory, concentration and focus.

Summer Banks has researched over 5000 weight-loss programs, pills, shakes and diet plans. Previously, she managed 15 supplement brands, worked with professionals in the weight loss industry and completed coursework in nutrition at Stanford University.